Threaded fasteners have become an integral part of modern engineering and construction practices. From securing heavy machinery to assembling everyday household items, threaded fasteners play a crucial role in ensuring structural integrity and reliability. If you're exploring the New York Times' (NYT) coverage or research on threaded fasteners, this article will serve as your ultimate guide to understanding their applications, types, and importance.
Whether you're an engineer, a DIY enthusiast, or simply curious about how threaded fasteners work, this article provides a detailed exploration of their functions and significance. We'll delve into the types of threaded fasteners, their applications, and why they are indispensable in various industries.
Join us as we uncover the world of threaded fasteners, their role in NYT's discussions, and how they contribute to the advancement of modern technology and infrastructure. By the end of this article, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of threaded fasteners and their impact on our daily lives.
Read also:Quantian Twitter Revolutionizing The Social Media Landscape
Here is a table of contents to help you navigate through this extensive guide:
- Introduction to Threaded Fasteners
- Types of Threaded Fasteners
- Materials Used in Threaded Fasteners
- Applications of Threaded Fasteners
- Threaded Fastener NYT Coverage
- Installation Techniques
- Maintenance and Inspection
- Standards and Regulations
- Advantages and Disadvantages
- Future Trends in Threaded Fasteners
Introduction to Threaded Fasteners
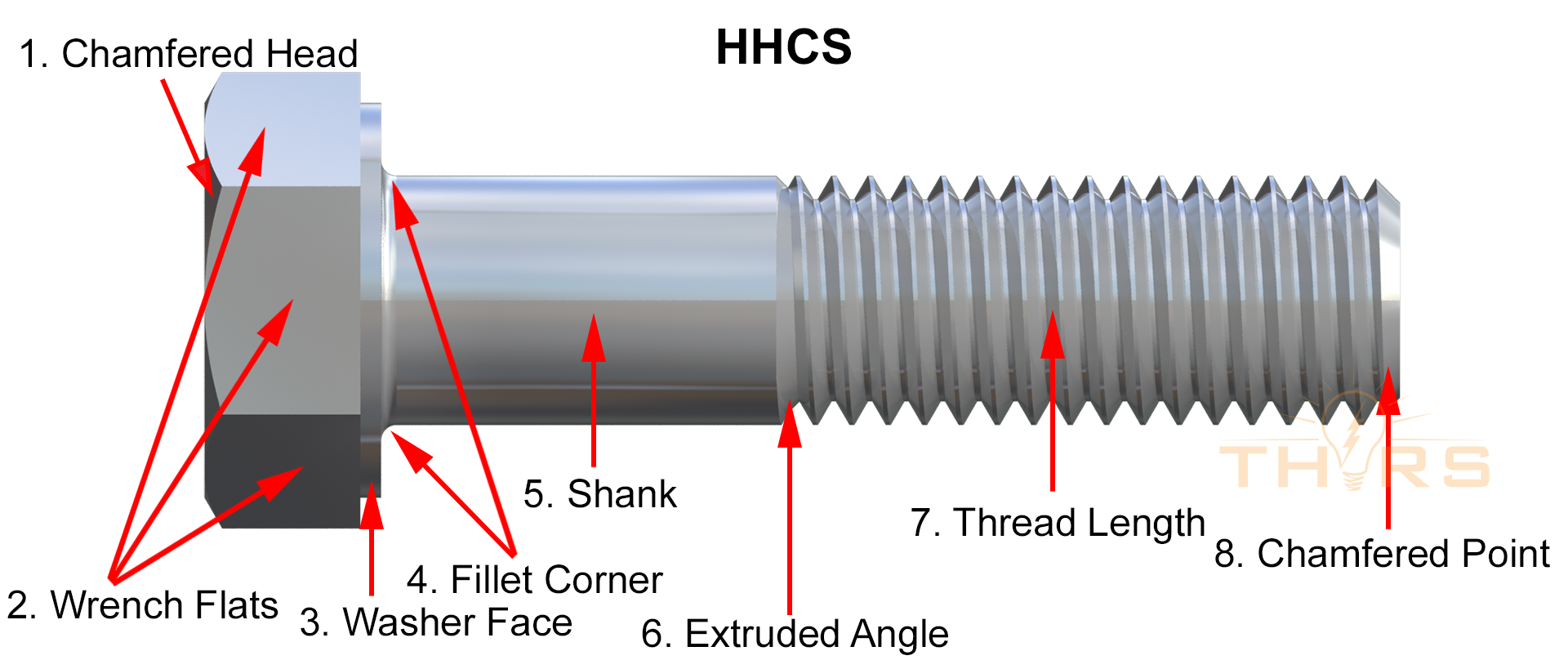
Threaded fasteners are mechanical devices designed to hold two or more objects together. They are characterized by their helical threads, which provide a secure and adjustable connection. Common examples include screws, bolts, and nuts. These fasteners are widely used in various industries, from automotive manufacturing to construction.
The importance of threaded fasteners cannot be overstated. They offer a reliable method of securing components, allowing for easy assembly and disassembly when needed. Understanding the basics of threaded fasteners is essential for anyone working in fields that require precision and durability.
Let's explore the fundamental aspects of threaded fasteners:
- Definition and function
- Key components and features li>Why threaded fasteners are preferred in industrial applications
Types of Threaded Fasteners
Common Types of Fasteners
Threaded fasteners come in various forms, each designed for specific applications. Below are some of the most common types:
- Bolts: Used with nuts to secure two unthreaded components.
- Screws: Often used to fasten materials by threading directly into the material.
- Nuts: Pair with bolts to provide a secure connection.
- Studs: Feature threads on both ends, commonly used in high-stress environments.
Specialized Fasteners
In addition to the standard types, there are specialized fasteners designed for specific industries:
Read also:Unpacking The Impact Of Megyn Kelly On Twitter A Comprehensive Analysis
- Aerospace fasteners
- Marine fasteners
- Medical-grade fasteners
Materials Used in Threaded Fasteners
The choice of material for threaded fasteners depends on the application and environmental conditions. Common materials include:
- Steel (carbon steel, stainless steel)
- Aluminum
- Brass
- Titanium
Each material offers unique properties, such as corrosion resistance, strength, and weight, making them suitable for different applications.
Applications of Threaded Fasteners
Industrial Applications
Threaded fasteners are indispensable in various industries:
- Automotive manufacturing
- Construction
- Electronics assembly
Consumer Applications
They are also widely used in consumer products:
- Furniture assembly
- Home improvement projects
Threaded Fastener NYT Coverage
The New York Times has occasionally covered topics related to threaded fasteners, particularly in discussions about industrial innovations and safety standards. These articles often highlight advancements in fastener technology and their impact on global industries.
For example, recent NYT articles have discussed the shift toward sustainable materials in fastener manufacturing and the importance of adhering to international standards.
Installation Techniques
Proper Installation Practices
Proper installation is critical to ensuring the effectiveness of threaded fasteners. Key techniques include:
- Torque control
- Surface preparation
- Thread lubrication
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Avoiding common mistakes during installation can prevent failures and ensure longevity:
- Over-tightening
- Using incorrect fastener sizes
Maintenance and Inspection
Regular maintenance and inspection of threaded fasteners are essential for safety and performance. Inspect for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage, and replace as necessary.
Standards and Regulations
Threaded fasteners must comply with various standards and regulations to ensure quality and safety. Key organizations include:
- ISO (International Organization for Standardization)
- ASTM International
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages
- Easy to install and remove
- Highly versatile
- Available in various materials and sizes
Disadvantages
- Prone to corrosion if not properly maintained
- Can loosen over time due to vibration
Future Trends in Threaded Fasteners
The future of threaded fasteners is shaped by advancements in materials science and manufacturing technology. Innovations such as self-healing coatings and smart fasteners with embedded sensors are on the horizon, promising to enhance performance and reliability.
Conclusion
In summary, threaded fasteners are vital components in modern engineering and construction. Their versatility, reliability, and adaptability make them indispensable across various industries. Understanding their types, applications, and proper usage ensures optimal performance and safety.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences with threaded fasteners in the comments section below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our site for more insights into engineering and technology topics.
Data and references used in this article are sourced from reputable organizations such as ASTM International and ISO, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the information provided.